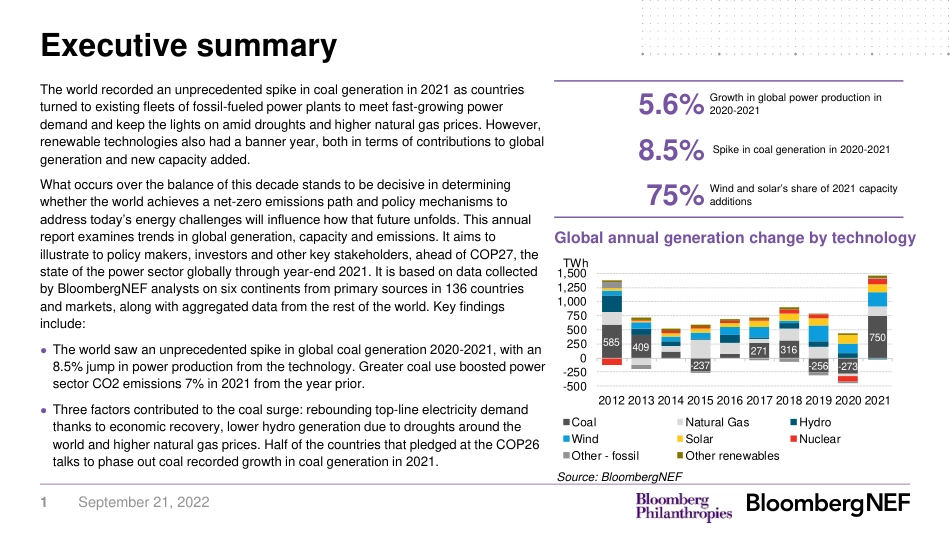
Power Transition Trends 2022Coal power spikes, but progress on renewables brings hopeSofia MaiaLuiza DemôroSeptember 21, 20221September 21, 2022The world recorded an unprecedented spike in coal generation in 2021 as countries turned to existing fleets of fossil-fueled power plants to meet fast-growing power demand and keep the lights on amid droughts and higher natural gas prices. However, renewable technologies also had a banner year, both in terms of contributions to global generation and new capacity added. What occurs over the balance of this decade stands to be decisive in determining whether the world achieves a net-zero emissions path and policy mechanisms to address today’s energy challenges will influence how that future unfolds. This annual report examines trends in global generation, capacity and emissions. It aims to illustrate to policy makers, investors and other key stakeholders, ahead of COP27, the state of the power sector globally through year-end 2021. It is based on data collected by BloombergNEF analysts on six continents from primary sources in 136 countries and markets, along with aggregated data from the rest of the world. Key findings include:● The world saw an unprecedented spike in global coal generation 2020-2021, with an 8.5% jump in power production from the technology. Greater coal use boosted power sector CO2 emissions 7% in 2021 from the year prior. ● Three factors contributed to the coal surge: rebounding top-line electricity demand thanks to economic recovery, lower hydro generation due to droughts around the world and higher natural gas prices. Half of the countries that pledged at the COP26 talks to phase out coal recorded growth in coal generation in 2021.Execu...