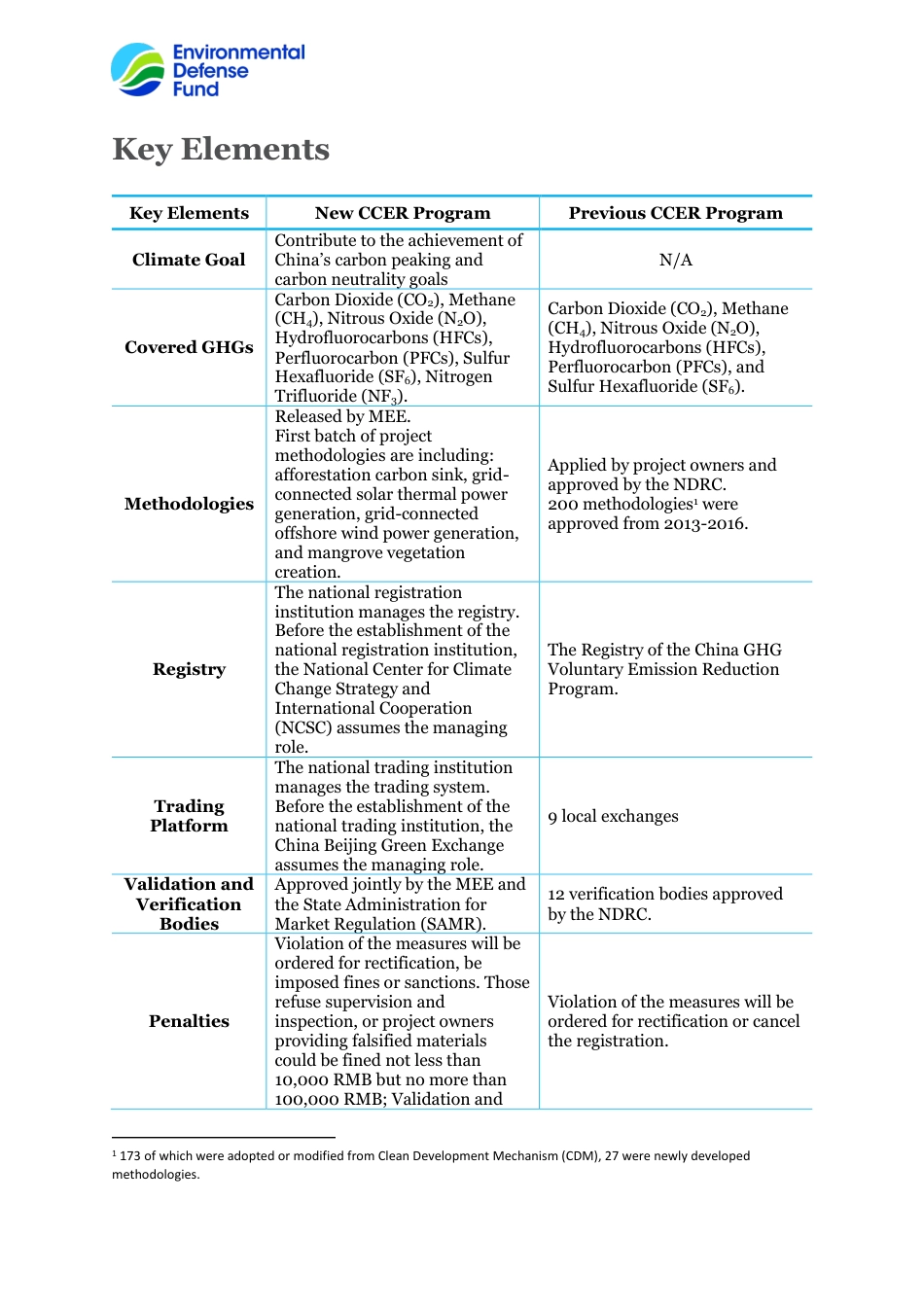
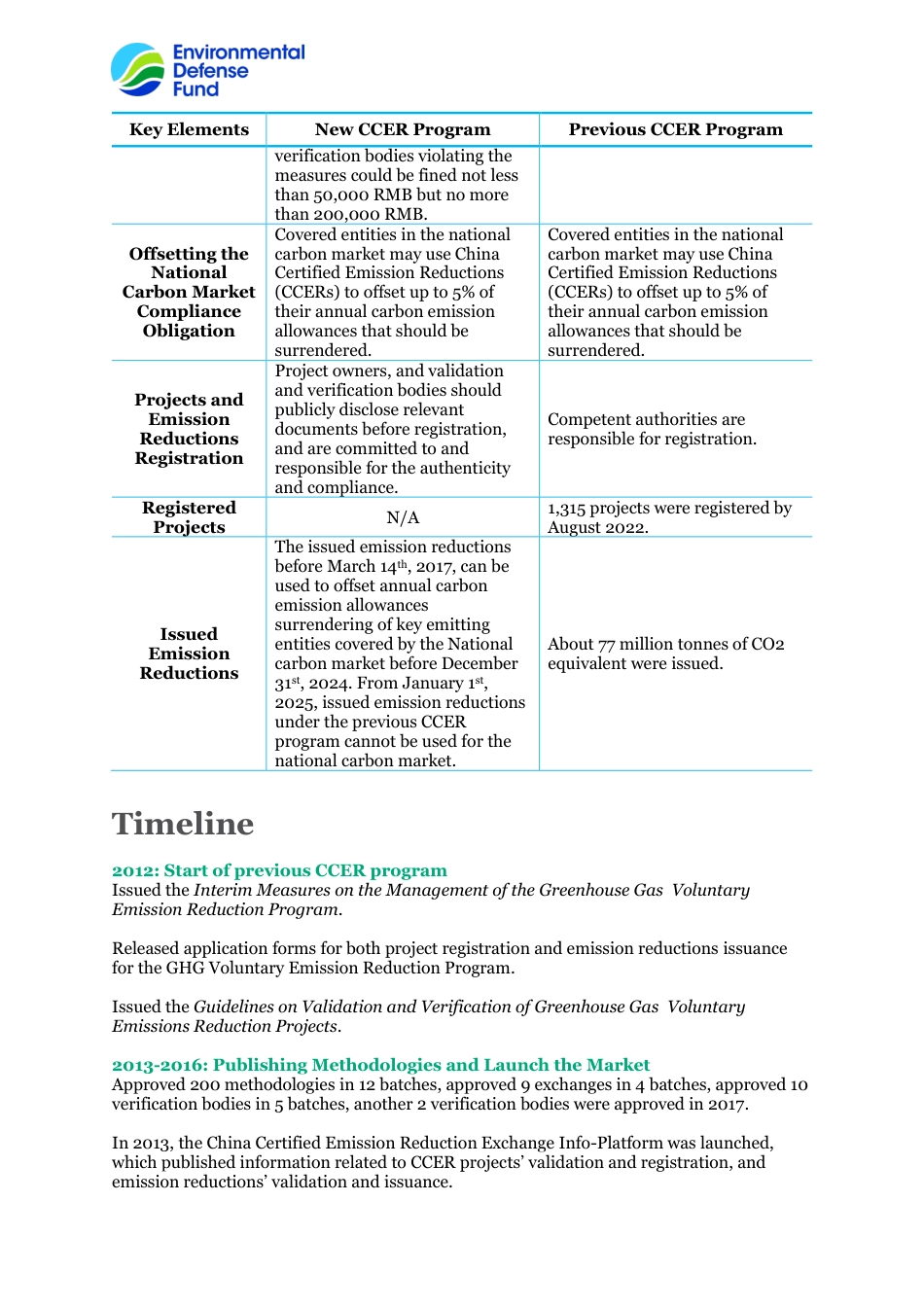
China GHG Voluntary Emission Reduction Program (CCER program) Fact Sheet As a supplemental option for the national and local compliance carbon markets, China GHG Voluntary Emission Reduction Program (CCER program) is able to help enterprises covered by compliance carbon markets fulfill their compliance obligation at a lower cost. CCER is also an important instrument for business or social activities that aims to achieve carbon neutrality for offsetting their hard-to-reduce emissions. Meanwhile, the financial benefits generated from the CCER projects can also incentivize ambitious emission reductions in the sectors not covered by compliance carbon markets, thereby accelerating the application of more low-cost emission reduction technologies and lowering the overall social emission reduction costs. In 2012, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) published the Interim Measures on the Management of the Greenhouse Gas Voluntary Emission Reduction Program and the Guidelines on Validation and Verification of Greenhouse Gas Voluntary Emissions Reduction Projects. In 2015, the national registry of Voluntary Carbon Emission Reductions was launched, marking the official start of trading for China's GHG Voluntary Emission Reduction Program. In 2017, NDRC suspended the new project development and credits issuance under the previous China's voluntary greenhouse gas emission reduction program (the previous CCER program). In 2018, the responsibilities of addressing climate change were transferred from the NDRC to the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE). The competent authority of managing the China GHG Voluntary Emission Reduction Program was shifted accordingly. Since the launch of previous CCER program in 2012, over...