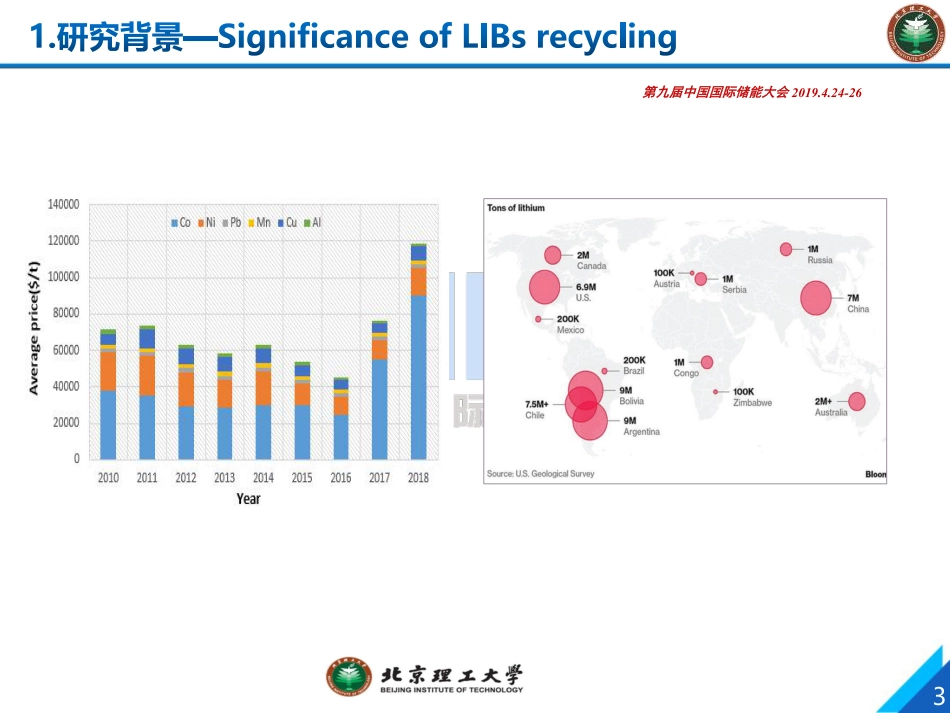
退役锂离子电池回收与资源化技术1E-mail: lily863@bit.edu.cn; wufeng863@bit.edu.cn李 丽 , 吴 锋*北京理工大学Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries: a review of current processes and technologies第九届中国国际储能大会2019.4.24-26 杭州 中国 行业发展与研究背景锂离子电池回收与再生技术 北理工课题组电池回收最新进展总结与展望第九届中国国际储能大会 2019.4.24-263第九届中国国际储能大会 2019.4.24-26CategoriesMaterialsPropertiesPotential environmental pollutionCathode materialLiCoO2/LiMn2O4/LiNiO2 /LiNiCoMnO2 Reacts with water, acids, reducing agents or strong oxidizing agents (hydrogen peroxide, chlorate, etc.) to produce harmful metal oxides.Heavy metal pollution raises the environmental pHAnode materialCarbon material / graphite, lithium intercalationin case of fire or high temperature, dust can explode and react with strong acid and strong alkali to produce gases such as CO and CO2.The CO and solid dust particles produced by the combustion of the anode material contaminate the air.ElectrolyteLiPF6/LiBF4/LiAsF6It is highly corrosive and can produce HF when exposed to water, and can be oxidized to produce toxic substances such as P2O5, Li2O, B2O3Fluorine pollution changes the pH of the environment, and the toxic gas generated pollutes the air and stimulates the human body through the skin and breathing.Electrolyte solventEthylene carbonate / Propylene carbonate / Dimethyl carbonateThe hydrolyzate produces aldehydes and acids, which can produce CO, CO2, etc.Organic matter such as aldehydes, ketones, and methanolSeparatorPP/PE Combustion can produce CO, aldehyde, etc.Organic pollutionBinderPVDF、VDF、EPD It can react with fluorine, fuming sulfuric acid, strong alkali, alkali metal, and decompose by heat to produce HF.Thermal decomposition produces HF and fluorine pollution...