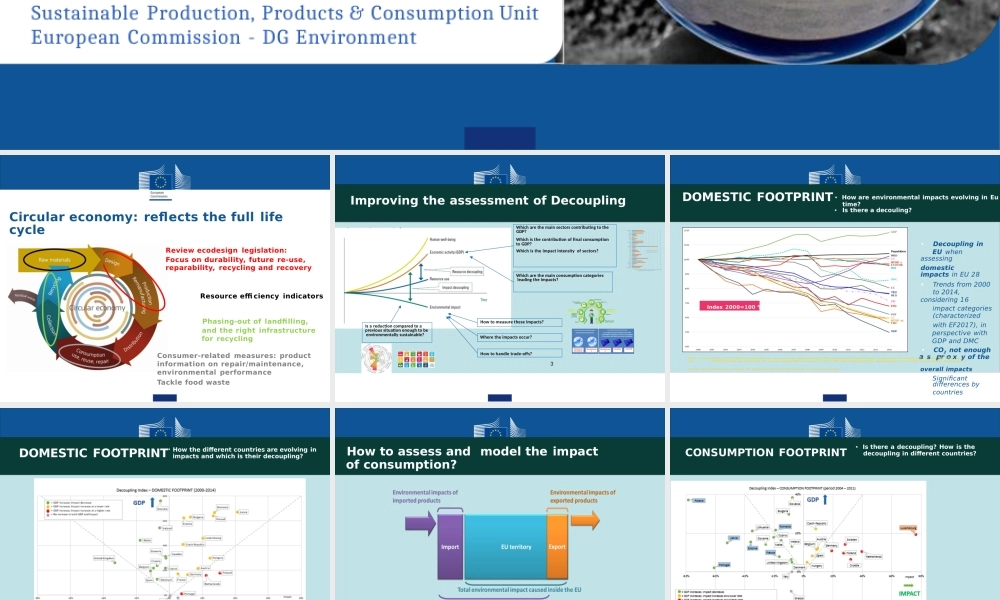
EuropeancommissionEnvironmental Footprintmethods: summary of asuccessful endeavorMichele GalatolaEnvironmental Footprint Team LeaderSustainable Production, Products & Consumption Unit European Commission - DG Environment★ ★★★★★★★★★ ★ ★Review ecodesign legislation:Focus on durability, future re-use, reparability, recycling and recoveryResource effi ciency indicatorsPhasing-out of landfilling,and the right infrastructure for recyclingConsumer-related measures: product information on repair/maintenance, environmental performanceTackle food wasteCircular economy: reflects the full life cycleWhich are the main sectors contributing to the GDP?Which is the contribution of final consumption to GDP?Which is the impact intensity of sectors?Improving the assessment of DecouplingWhich are the main consumption categories leading the impacts?Is a reduction compared to aprevious situation enough to be environmentally sustainable?How to measure these impacts?Where the impacts occur?How to handle trade-offs?3• Decoupling in EU whenassessingdomesticimpacts in EU 28• Trends from 2000 to 2014,considering 16impact categories (characterizedwith EF2017), in perspective with GDP and DMC• CO2 not enoughHTOX_c: human toxicity, cancer; HTOX_nc: human toxicity, non cancer; PM: particulate matter; POF: photochemical ozone formation, human health; IR: ionising ra iastion; : axtery of theuse; ECOTOX; ecotoxicity, freshwater; CC: climate change; FRD: resource use, fossil; ODP: ozone depletion; MEU: eutrophication, marine; FEU: eutrophication, freshwater; LU:land use; TEU: eutrophication, terrestrial; AC: acidification terrestrial; MRD: resource use, minerals and metals. overall impactsSignificantDOMESTIC FOOTPRINT • How are environmental impacts evolving in Eu time?• Is th...