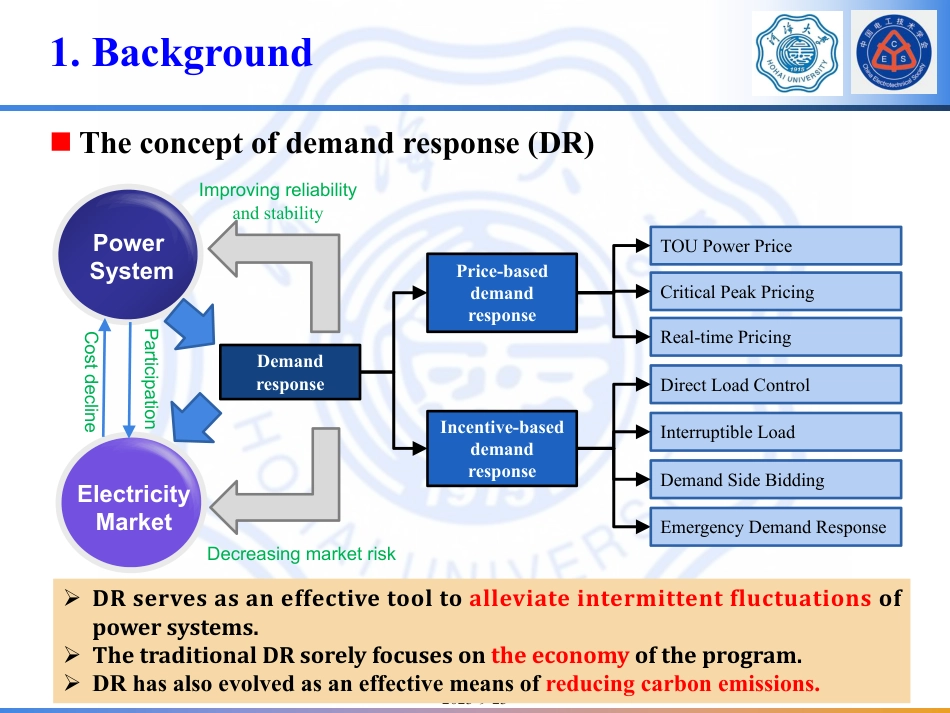
综合能源用户污染气体扩散评估及其参与需求响应模型吴英俊河海大学第十八届中国电工技术学会学术年会22023-9-23OutlineBackground1Problem formulation & Motivation2345MethodologyCase studiesConclusion32023-9-231. Backgroundn The concept of demand response (DR)Demand responseIncentive-based demand responsePrice-based demand responseInterruptible LoadTOU Power PriceCritical Peak PricingReal-time PricingDirect Load ControlDemand Side BiddingEmergency Demand ResponsePower SystemElectricityMarketImproving reliability and stabilityDecreasing market riskParticipationCost declineØ DR serves as an effective tool to alleviate intermittent fluctuations of power systems.Ø The traditional DR sorely focuses on the economy of the program.Ø DR has also evolved as an effective means of reducing carbon emissions.42023-9-231. Background – Research gapn Remark 1: carbon emission of the ICs in the DR is rarely considered in the current studiesl Utilize the DR technology to reduce carbon emission on the generation side while ignore the emission on the load sidel The main participants of the DR are industrial customers (ICs), whose main energy consumption relies on fossil fuelsn Remark 2: the influences of pollutants released by the ICs cannot be neglected in the DR scheduling designl In the DR, apart from CO2 emissions, there are also some pollutants released by ICsl SO2, CO, and NOx from incomplete ignition of fuelsl other greenhouse gases (fluorinated gases: hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, SF6, NF3; CH4) from chemical production52023-9-232. Problem descriptionn How to select ICs to participate in DR with a minimum cost while reducing the environmental influences of the pollutantsCurrent researchTraditional solution: Ø add an extra cost into the objective functionRese...