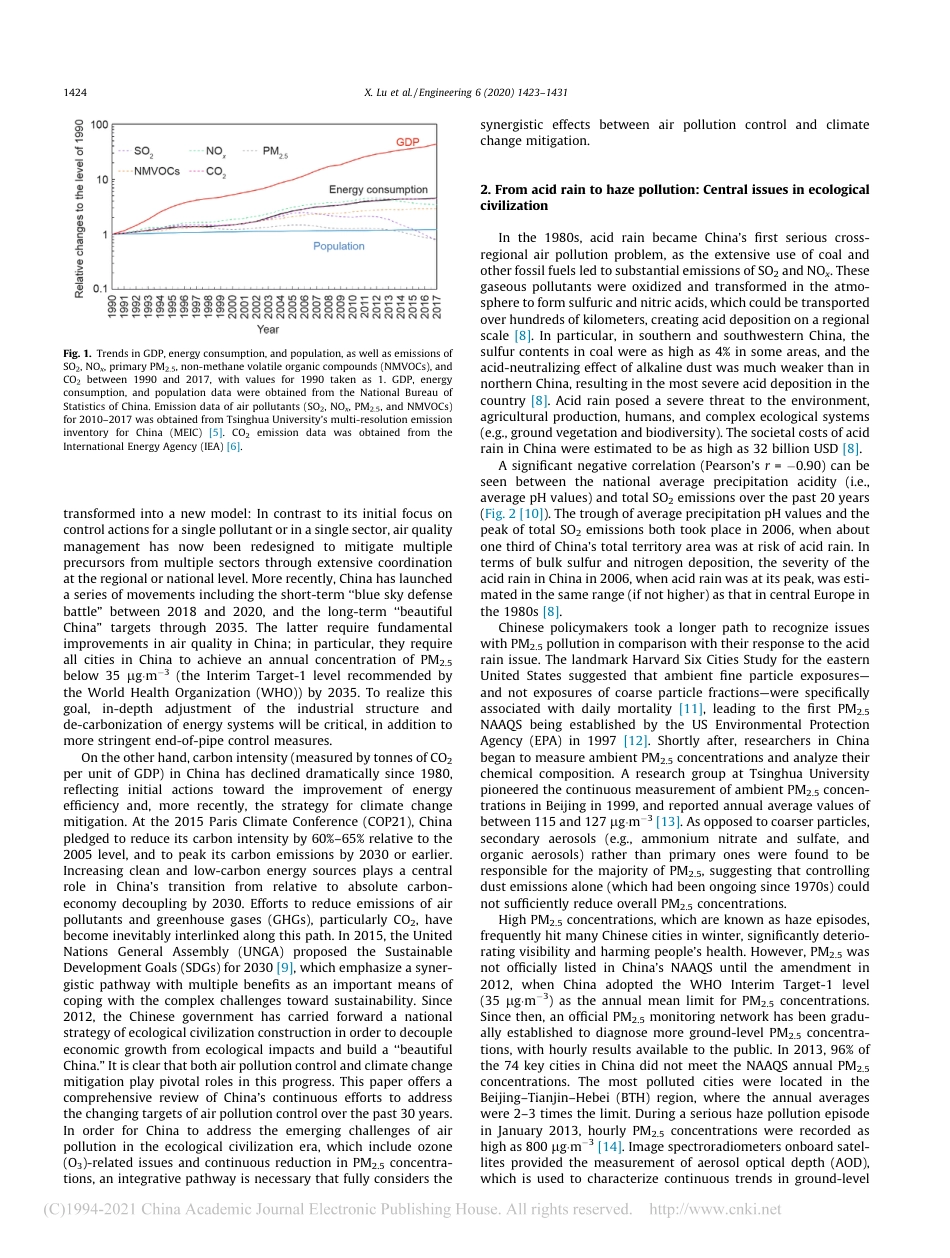
ResearchAir Pollution Control—ReviewProgress of Air Pollution Control in China and Its Challenges andOpportunities in the Ecological Civilization EraXi Lu a,b,#, Shaojun Zhang a,b,#, Jia Xing a,b,#, Yunjie Wang a, Wenhui Chen a, Dian Ding a, Ye Wu a,b,Shuxiao Wang a,b,⇑, Lei Duan a,b, Jiming Hao a,b,⇑a State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control, School of Environment, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, Chinab State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Sources and Control of Air Pollution Complex, Beijing 100084, Chinaa r t i c l ei n f oArticle history:Received 27 December 2019Revised 18 March 2020Accepted 26 March 2020Available online 19 June 2020Keywords:Air pollution controlEcological civilizationPM2.5Low-carbon developmentOzonea b s t r a c tChina’s past economic growth has substantially relied on fossil fuels, causing serious air pollution issues.Decoupling economic growth and pollution has become the focus in developing ecological civilization inChina. We have analyzed the three-decade progress of air pollution controls in China, highlighting astrategic transformation from emission control toward air quality management. Emission control of sul-fur dioxide (SO2) resolved the deteriorating acid rain issue in China in 2007. Since 2013, control actionson multiple precursors and sectors have targeted the reduction of the concentration of fine particulatematter (PM2.5), marking a transition to an air-quality-oriented strategy. Increasing ozone (O3) pollutionfurther requires O3 and PM2.5 integrated control strategies with an emphasis on their complex photo-chemical interactions. Fundamental improvement of air quality in China, as a key indicator for the suc-cess of ecological civilizat...